Science Badges:
'Conservation'
Climate Science
Global Warming
Recycling
Renewable Energy
Fossil Fuels
Ecology
Our Planet
Water
Plants
15 Points are needed to get a badge
A high standard of work.
All experiments are written up ( Aim, Materials, Steps, Conclusion)
Two photos of your experiment
6 sentences at least for a conclusion
Science will be twice per week.
Lesson 1: This will be an Experiment that involves blogging. You will be expected to open a new post, copy Mr Palmer's blog and paste it on your new post.
Lesson 2: This will be an Investigation that relates to the topic from Lesson 1. It will be own choice and displayed in a way that you prefer. For example - PowerPoint, Doc, etc
Expectations:
1 blog must be completed per Hurumanu lesson.
A completed blog must have the four headings ( Aim, Method, Findings, Conclusion), correct writing and punctuation under each heading and be published. No post, no points.
2 images of the experiment / investigation on the blog.
Using the Scientific method of investigation:
Aim: What the experiment / investigation is about.
Method: Instructions on how the experiment / investigation is carried out. This includes the equipment.
Findings: What have we learnt or found out from our experiment / investigation. This is called Data, Information or Facts. It is displayed in a chart, table or picture.
Conclusion: Two Huramanu science goals:
To always add photos to my posts
To make sure that I'm in my readers shoes and make sure they understand what I have wrote
to make sure that I have great punctuation
to try and get a science badge
THE BIG PICTURE
What animals keep our jackets warm?
What animal makes our boots waterproof?
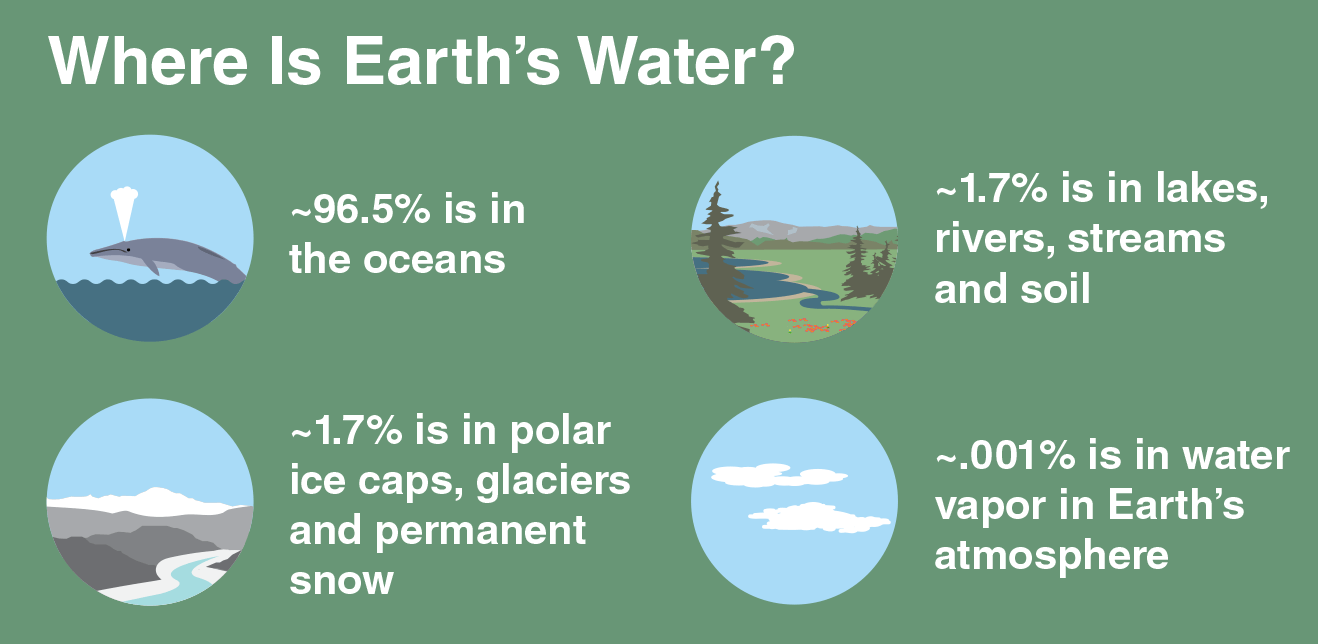
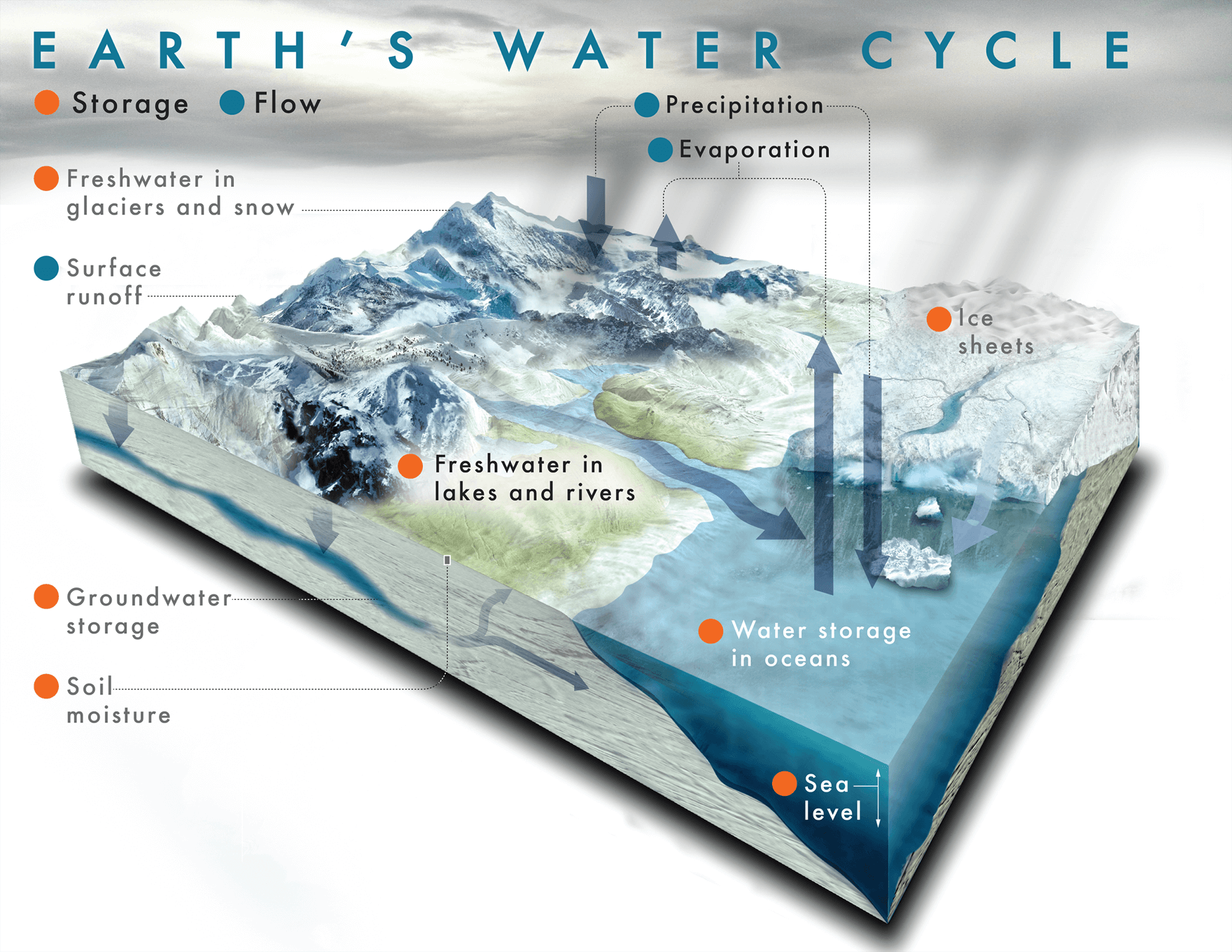
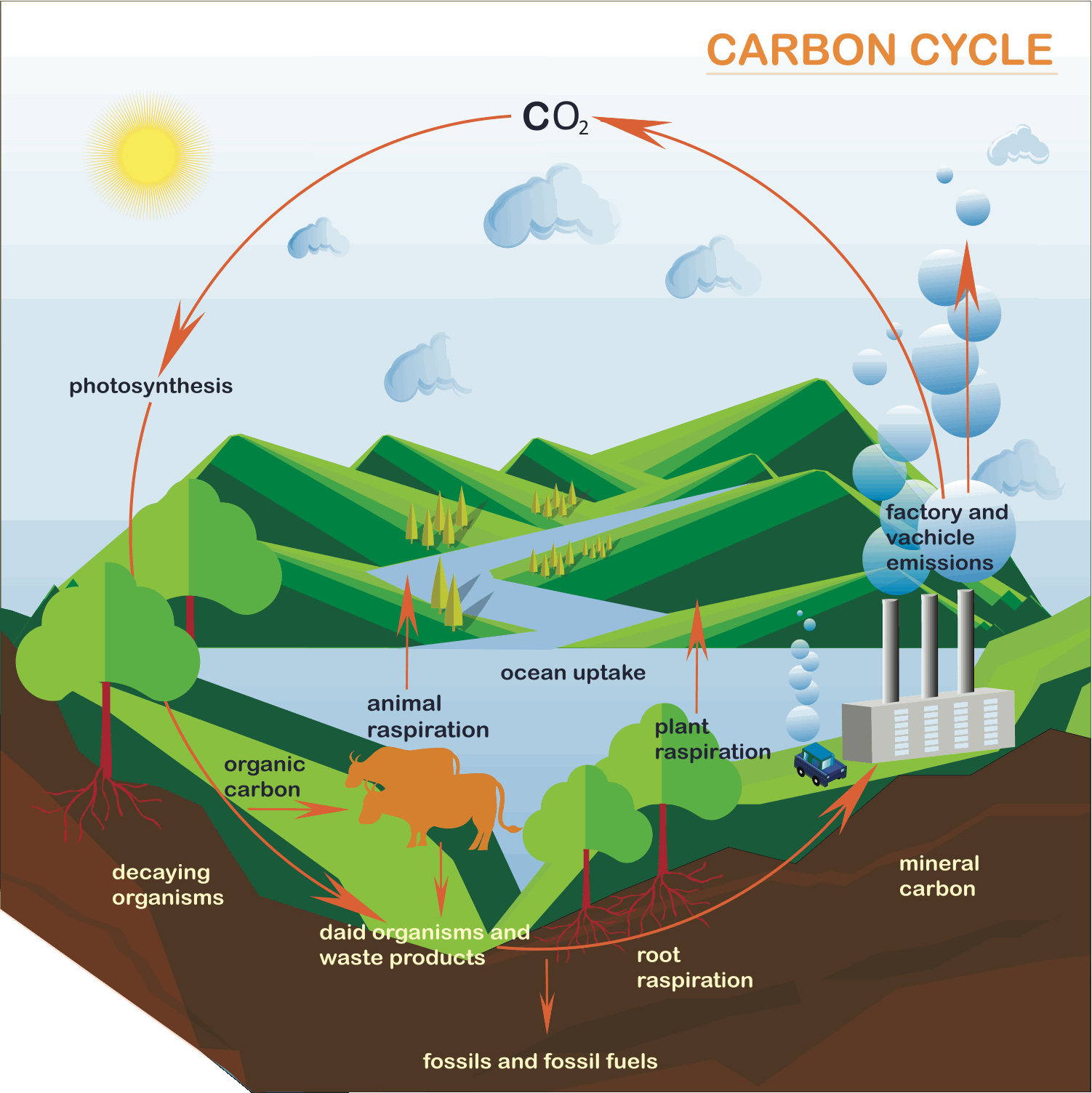
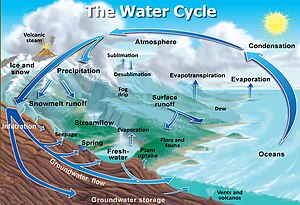
Where does the water in our rivers come from?
What are some of the good things about mosquitoes?
Why are bees dying?
What do bugs do to our leaves
How much dung would we be in if there were no dung de- composers?
Who runs this planet?
GROUP ACTIVITY;
Groups of 3 or 4 students.
Need A3 copy paper.
THE ICECAPS HAVE MELTED. MOST OF THE LAND IN THE WORLD HAS BEEN FLOODED AND YOU AND YOUR FRIENDS ARE ON A BOAT IN THE MIDDLE OF KNOW WHERE. YOUR BOAT IS SUDDENLY STRUCK BY A STORM AND YOU BECOME SHIPWRECKED ON A SMALL ISLAND. YOU ARE ONLY ALOUD TO SELECT 20 ITEMS FOR YOUR GROUP. A SECOND BOAT IS TRAVELLING NEAR YOU BUT WILL NOT BE ABLE TO REACH YOU FOR 1 MONTH SO YOU NEED TO GATHER ENOUGH SUPPLIES TO LAST FOR A MONTH.
In your group you need to:
1. Make a list of the 10 things you are going to collect.
2. Draw a map of the island.
4. Draw and label the activities you will be involved with.